Introduction
The Center for Internet Security provides many guidelines and benchmark tests for best practices in securing your code. The CIS has published a benchmark for Kubernetes. The kube-bench is an open-source tool that checks whether Kubernetes is deployed securely by running the CIS benchmark for Kubernetes checks. It's written as a Go application and also distributed as a container. Each test is defined in the YAML and also supports JSON-format output that can be used to evolve along wiht Kubernetes and to integrate with automaton tools.
Managed Kubernetes & CIS Amazon EKS Benchmark
The CIS Kubernetes Benchmark is scoped for implementations managing both the control plane, which includes etcd, API server, controller, scheduler, and the data plane, which is made up of one or more nodes or EC2 instances.
The managed Kubernetes clusters provide a level of CIS hardening already in place, and it delegates some settings to the user. It works best when you want to understand whether your workloads and the worker nodes are appropriately set up to implement these guidelines. CIS Amazon EKS Benchmark v1.0.0 provides guidance for node security configurations for Kubernetes and aligns with CIS Kubernetes Benchmark.
Running kube-bench
We will deploy the Kubernetes Job using the below YAML file. We can install the kube-bench directly in the nodes as well. In this blog, we are going to run the kube-bench as a kubernetes job.
# eks-kube-bench-job.yaml
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
name: kube-bench
spec:
template:
spec:
hostPID: true
containers:
- name: kube-bench
image: aquasec/kube-bench:latest
command: ["kube-bench", "--benchmark", "eks-1.0"]
volumeMounts:
- name: var-lib-kubelet
mountPath: /var/lib/kubelet
readOnly: true
- name: etc-systemd
mountPath: /etc/systemd
readOnly: true
- name: etc-kubernetes
mountPath: /etc/kubernetes
readOnly: true
restartPolicy: Never
volumes:
- name: var-lib-kubelet
hostPath:
path: "/var/lib/kubelet"
- name: etc-systemd
hostPath:
path: "/etc/systemd"
- name: etc-kubernetes
hostPath:
path: "/etc/kubernetes"
Run the job in your EKS cluster
kubectl apply -f eks-kube-bench-job.yaml
Once the kube-bench job is completed, you can view the pod's logs to see the results of the kube-bench.
[INFO] 3 Worker Node Security Configuration
[INFO] 3.1 Worker Node Configuration Files
[PASS] 3.1.1 Ensure that the proxy kubeconfig file permissions are set to 644 or more restrictive (Scored)
[PASS] 3.1.2 Ensure that the proxy kubeconfig file ownership is set to root:root (Scored)
[PASS] 3.1.3 Ensure that the kubelet configuration file has permissions set to 644 or more restrictive (Scored)
[PASS] 3.1.4 Ensure that the kubelet configuration file ownership is set to root:root (Scored)
[INFO] 3.2 Kubelet
[PASS] 3.2.1 Ensure that the --anonymous-auth argument is set to false (Scored)
[PASS] 3.2.2 Ensure that the --authorization-mode argument is not set to AlwaysAllow (Scored)
[PASS] 3.2.3 Ensure that the --client-ca-file argument is set as appropriate (Scored)
[PASS] 3.2.4 Ensure that the --read-only-port argument is set to 0 (Scored)
[PASS] 3.2.5 Ensure that the --streaming-connection-idle-timeout argument is not set to 0 (Scored)
[PASS] 3.2.6 Ensure that the --protect-kernel-defaults argument is set to true (Scored)
[PASS] 3.2.7 Ensure that the --make-iptables-util-chains argument is set to true (Scored)
[PASS] 3.2.8 Ensure that the --hostname-override argument is not set (Scored)
[WARN] 3.2.9 Ensure that the --event-qps argument is set to 0 or a level which ensures appropriate event capture (Scored)
[PASS] 3.2.10 Ensure that the --rotate-certificates argument is not set to false (Scored)
[PASS] 3.2.11 Ensure that the RotateKubeletServerCertificate argument is set to true (Scored)
== Remediations ==
3.2.9 If using a Kubelet config file, edit the file to set eventRecordQPS: to an appropriate level.
If using command line arguments, edit the kubelet service file
/etc/systemd/system/kubelet.service on each worker node and
set the below parameter in KUBELET_SYSTEM_PODS_ARGS variable.
Based on your system, restart the kubelet service. For example:
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl restart kubelet.service
== Summary ==
14 checks PASS
0 checks FAIL
1 checks WARN
0 checks INFO
Delete the job
Run the below commands to delete the kube-bench job.
kubectl delete -f job-eks.yaml
Integrating kube-bench with AWS Security Hub
You can configure kube-bench with the --asff to send findings to AWS Security Hub. Before, that, we've to enable the AWS Security Hub integration and set the required IAM role and policies to forward the findings to the AWS Security Hub.
Enable the AWS Security Hub integration
You will need AWS Security Hub to be enabled in your account. In the Security Hub console, under Integrations, search for kube-bench. Click on Accept findings to enable the "Aqua Security kube bench" to integrate with AWS Security Hub.
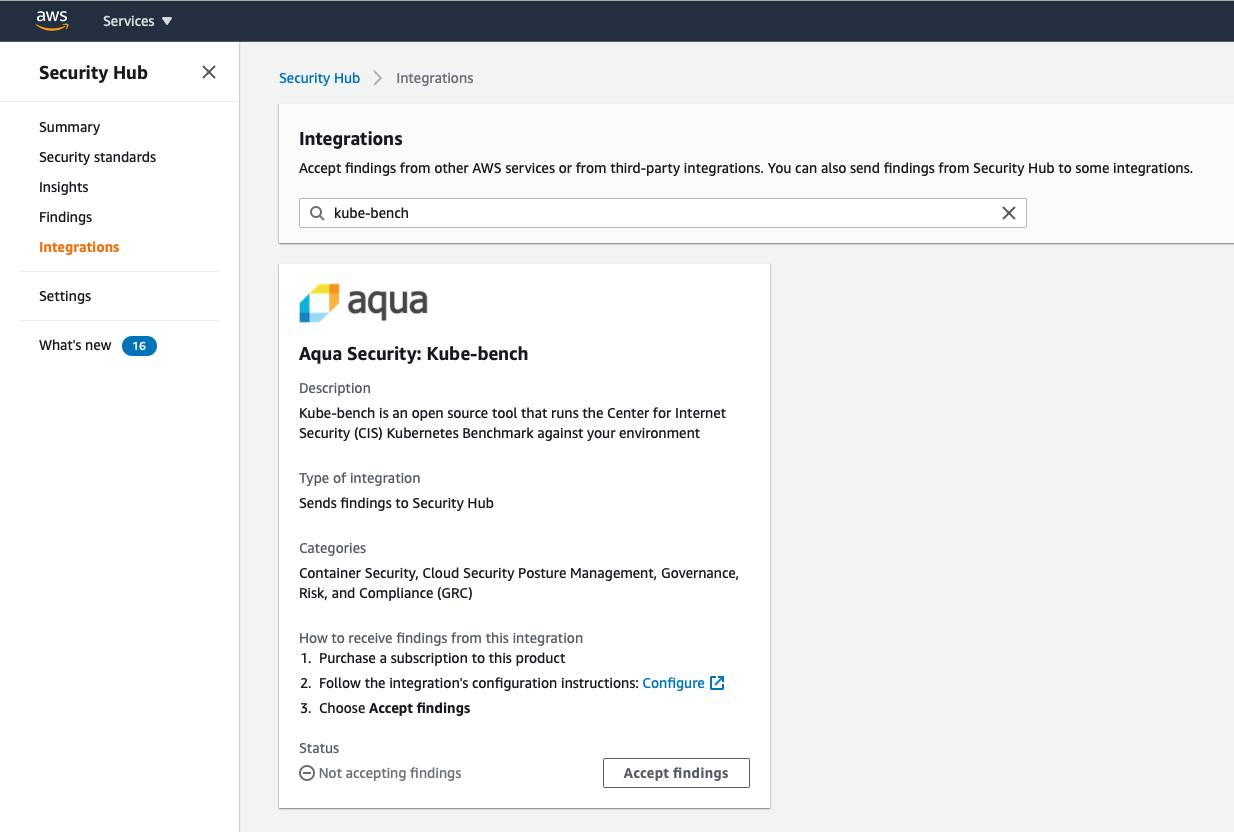
Now let's configure the kube-bench job to send the report to AWS Security Hub.
IAM Policy to send to AWS Security Hub
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "securityhub:BatchImportFindings",
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:securityhub:us-east-1::product/aqua-security/kube-bench"
]
}
]
}
Create Service Account IAM Role and Policy
Please use this guide creating the IAM role and policy to attach to the service account for the pod running the kube-bench job.
kube-bench with asff
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: kube-bench
# If using a dedicated IAM role for kube-bench, uncomment the annotations
# block below and replace the ROLE_ARN
# annotations:
# eks.amazonaws.com/role-arn: "<ROLE_ARN>"
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: kube-bench-eks-config
data:
config.yaml: |
AWS_ACCOUNT: "<AWS_ACCT_NUMBER>"
AWS_REGION: "<AWS_REGION>"
CLUSTER_ARN: "<AWS_CLUSTER_ARN>"
---
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
name: kube-bench
spec:
template:
spec:
hostPID: true
containers:
- name: kube-bench
image: aquasec/kube-bench:latest
command: ["kube-bench", "node", "--benchmark", "eks-1.0", "--asff"]
volumeMounts:
- name: var-lib-kubelet
mountPath: /var/lib/kubelet
readOnly: true
- name: etc-systemd
mountPath: /etc/systemd
readOnly: true
- name: etc-kubernetes
mountPath: /etc/kubernetes
readOnly: true
- name: kube-bench-eks-config
mountPath: "/opt/kube-bench/cfg/eks-1.0/config.yaml"
subPath: config.yaml
readOnly: true
restartPolicy: Never
serviceAccountName: kube-bench
volumes:
- name: var-lib-kubelet
hostPath:
path: "/var/lib/kubelet"
- name: etc-systemd
hostPath:
path: "/etc/systemd"
- name: etc-kubernetes
hostPath:
path: "/etc/kubernetes"
- name: kube-bench-eks-config
configMap:
name: kube-bench-eks-config
items:
- key: config.yaml
path: config.yaml
Run the job using the above yaml to send the findings to AWS Security Hub.
Security Hub Findings
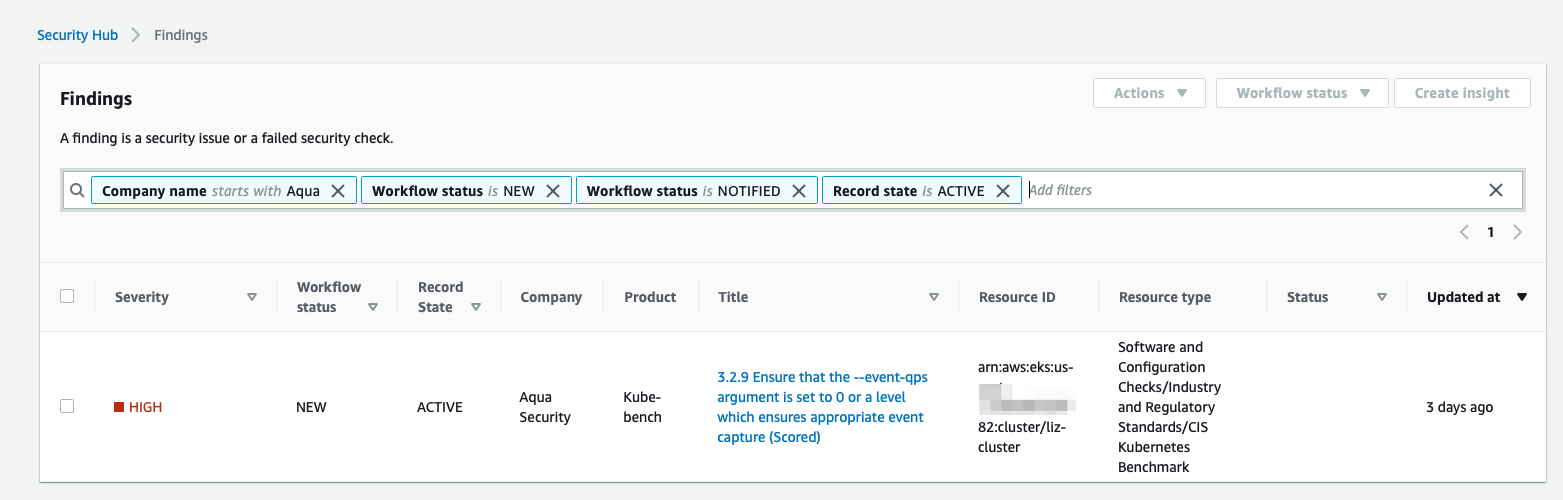
Conclusions
In this blog post, we had a walkthrough on running kube-bench tests against EKS worker nodes and forwarding the kube-bench summary to AWS Security Hub. You can use the CIS Amazon EKS Benchmark to assess Amazon EKS cluster nodes' security configuration accurately.
